🗓️ This Week In AI Research (23-29 November 25)
The top 10 AI research papers that you must know about this week.
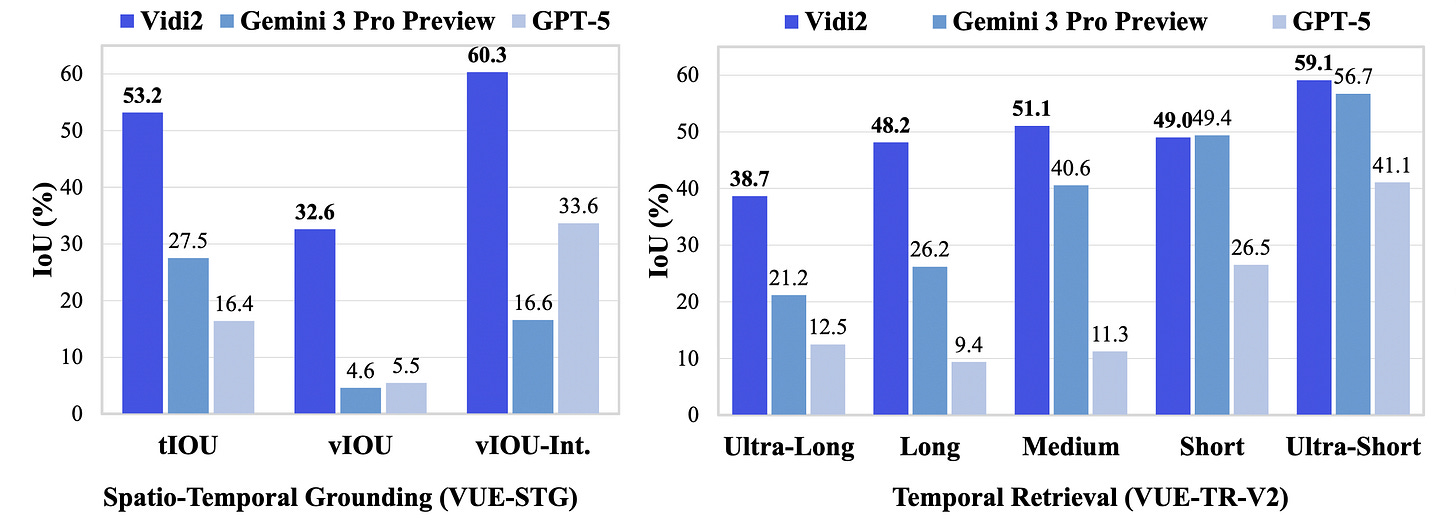
1. Vidi2: Large Multimodal Models for Video Understanding and Creation
This research from ByteDance introduces Vidi2, an AI model designed for advanced multimodal video reasoning.
The model achieves the following three tasks with state-of-the-art accuracy:
Temporal Retrieval (TR): Finding when events occur in videos
Spatio-Temporal Grounding (STG): Identifying both when and where objects appear (timestamps + bounding boxes) in response to text queries
Video Question Answering
The researchers also present VUE-STG, a new benchmark with long, richly annotated videos to evaluate its capabilities.
They also upgrade the earlier VUE-TR benchmark to VUE-TR-V2, adding more balanced video lengths and more natural user-style queries.
Vidi2 outperforms leading proprietary models like Gemini 3 Pro (Preview) and GPT-5 on both VUE-TR-V2 and VUE-STG, while matching the performance of similarly sized open-source models on video QA tasks.
Read more about this research using this link.
Before we move forward, I want to introduce you to my book, ‘LLMs In 100 Images’.
It is a collection of 100 easy-to-follow visuals that explain the most important concepts you need to master to understand LLMs today.
Grab your copy today using this link.
2. Claude Opus 4.5
Claude Opus 4.5 is Anthropic’s newest LLM, with major improvements in coding, reasoning, and computer-use tasks.
It achieves state-of-the-art performance on software engineering benchmarks and outscores all human candidates on Anthropic’s internal two-hour coding test.
Despite being more capable, it’s also significantly cheaper, more token-efficient, strongly aligned, and resistant to prompt-injection attacks.
Read more about it using this link.
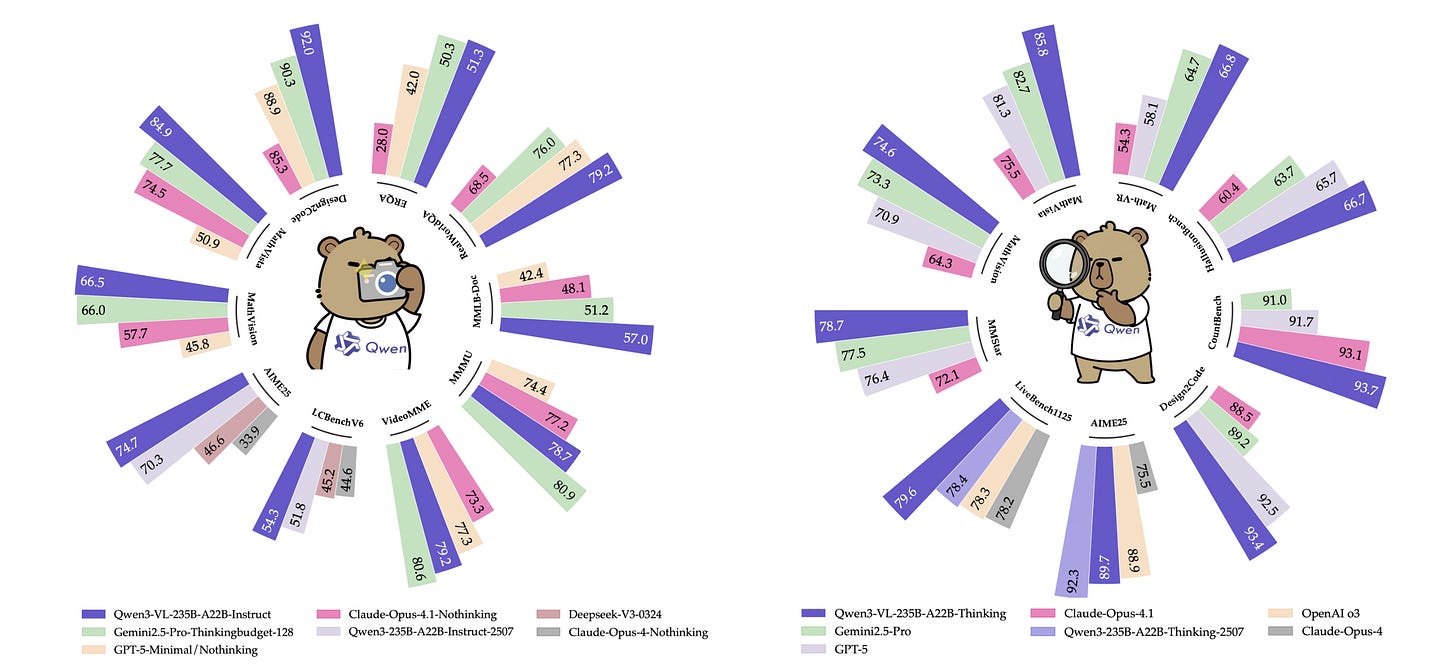
3. Qwen3-VL Technical Report
This research introduces Qwen3-VL, the most capable vision–language model in Alibaba’s Qwen series to date.
The model can handle extremely large multimodal inputs in text, images, and video with support for 256K interleaved tokens.
The model comes in multiple sizes, including both dense and mixture-of-experts variants, and has three major strengths:
Stronger pure-text understanding
Robust long-context comprehension
State-of-the-art multimodal reasoning across images and video
Read its technical report using this link.
4. Latent Collaboration in Multi-Agent Systems
This research introduces LatentMAS, a training-free framework that enables multiple LLM agents to collaborate by sharing latent representations instead of exchanging text.
Each agent generates “latent thoughts” from its hidden embeddings, which are stored in a shared latent memory for lossless information exchange.
Across nine benchmarks in reasoning, commonsense, and code generation, LatentMAS achieves up to 14.6% higher accuracy, uses 70–84% fewer output tokens, and delivers 4–4.3× faster inference.
This improved reasoning quality comes with increased efficiency, without requiring any additional training.
Read more about this research using this link.
5. AlphaFold: Five years of impact
It has been 5 years since the introduction of AlphaFold, the first AI system that can reliably predict a protein’s 3D structure from only its amino acid sequence.
AlphaFold has since been used to predict more than 200 million protein structures and create the AlphaFold Protein Database, achieving what would take hundreds of millions of years to determine and develop experimentally.
Millions of researchers have used these freely available protein structures in 190+ countries, leading to large-scale advances, including:
Designing enzymes that break down plastics more efficiently
Designing drugs effective against human diseases
Mapping the structure of apoB100, the key protein in “bad cholesterol”, which will help researchers develop more targeted treatments for the condition
Mapping the structure of a vital protein called Vitellogenin (Vg) in honeybees, which will help scientists breed bees that are more disease-resistant and stress-tolerant
Read more about Alphafold’s impact using this link.
Here’s
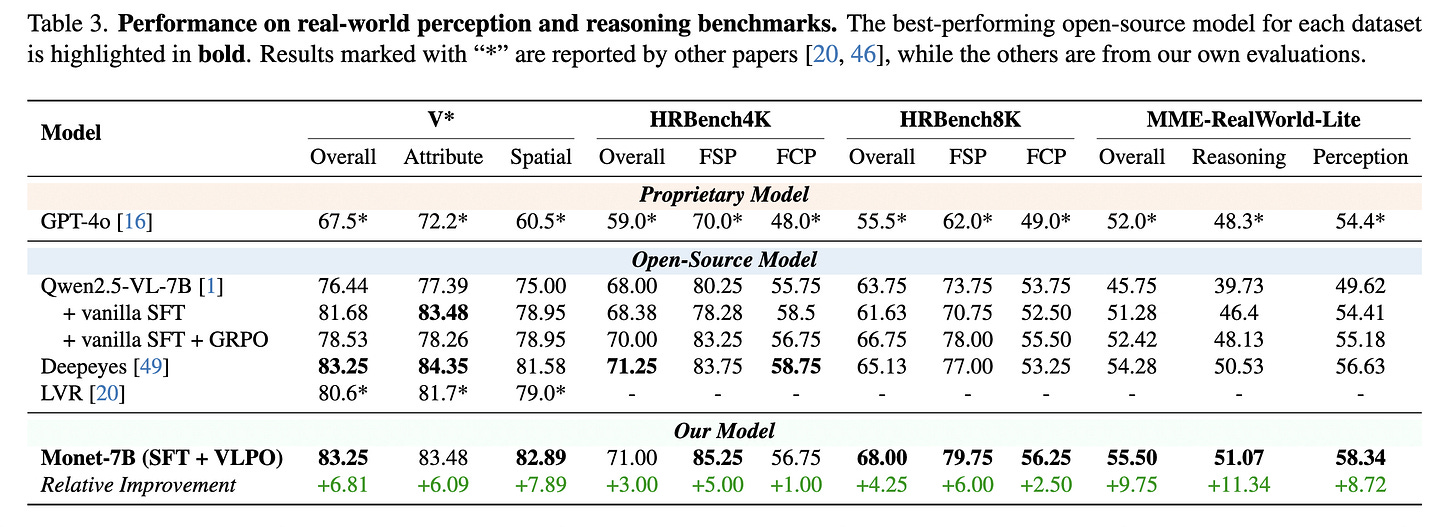
6. Monet: Reasoning in Latent Visual Space Beyond Image and Language
Monet is a training framework that teaches multimodal LLMs to reason directly in a visual latent space.
Instead of producing words for intermediate reasoning steps, Monet generates continuous visual embeddings that act as “visual thoughts”.
To make this possible, researchers use a three-stage distillation-based SFT pipeline and introduce VLPO (Visual Latent Policy Optimization), a reinforcement learning algorithm that updates policies using both text and latent visual embeddings.
Researchers build Monet-SFT-125K, a large 125k interleaved text-image chain-of-thought dataset covering real images, charts, OCR, and geometry.
This dataset is used to train Monet-7B, which achieves consistent improvements on perception, reasoning, and challenging abstract visual tasks, with strong out-of-distribution generalization.
Read more about this research using this link.
7. HunyuanOCR Technical Report
This research from Tencent introduces HunyuanOCR, a 1B-parameter vision-language model for OCR and document understanding tasks.
It is built with a native-resolution ViT encoder and a small language model connected through an MLP adapter. This design enables it to read and interpret documents without the multi-stage pipelines used in traditional OCR systems, reducing errors and simplifying deployment.
Despite its small size, HunyuanOCR achieves state-of-the-art results across tasks such as text recognition, document parsing, information extraction, and visual question answering, outperforming many larger vision-language models.
Read its technical report using this link.
8. ToolOrchestra: Elevating Intelligence via Efficient Model and Tool Orchestration
This research from NVIDIA introduces ToolOrchestra, a method for training small “orchestrator” models that decide which external tools or specialized models to invoke at each step of solving a complex task.
Using reinforcement learning with ToolOrchestra, the researchers trained an 8B model called Orchestrator that achieves 37.1% accuracy on Humanity’s Last Exam, outperforming GPT-5’s 35.1% while being 2.5x more efficient.
Read more about this research using this link.
9. Adversarial Confusion Attack: Disrupting Multimodal Large Language Models
This research introduces the Adversarial Confusion Attack, a new class of attack against multimodal LLMs that reduces their reliability by forcing them to produce incoherent or confidently incorrect responses.
The attack uses a single adversarial image that maximizes the LLM's next-token entropy, causing the model’s reasoning to break down when it encounters the image.
The attack transfers successfully to both open-source models (e.g., Qwen3-VL) and proprietary models (e.g., GPT-5.1).
Read more about this research using this link.
10. DR Tulu: Reinforcement Learning with Evolving Rubrics for Deep Research
This research from Allen AI introduces Reinforcement Learning with Evolving Rubrics (RLER), an RL algorithm to train LLMs to perform deep, long-form research tasks.
Rather than relying on fixed evaluation criteria, RLER constructs and continuously updates rubrics that co-evolve with the policy model, ensuring that feedback remains relevant as the model becomes more capable.
Using RLER, researchers trained Deep Research Tulu (DR Tulu-8B), the first open model directly trained for open-ended, long-form deep research.
DR Tulu outperforms existing open deep research models, and matches or exceeds several proprietary deep research systems, across four long-form deep research benchmarks in science, healthcare, and general domains, while being significantly smaller and cheaper per query.
Read more about this research using this link.
This article is free to read. If you loved reading it, restack it and share it with others.💚
If you want to get even more value from this publication, become a paid subscriber and unlock all posts.
You can also check out my books on Gumroad and connect with me on LinkedIn to stay in touch.