🗓️ This Week In AI Research (18-24 January 26)
The top 10 AI research papers that you must know about this week.
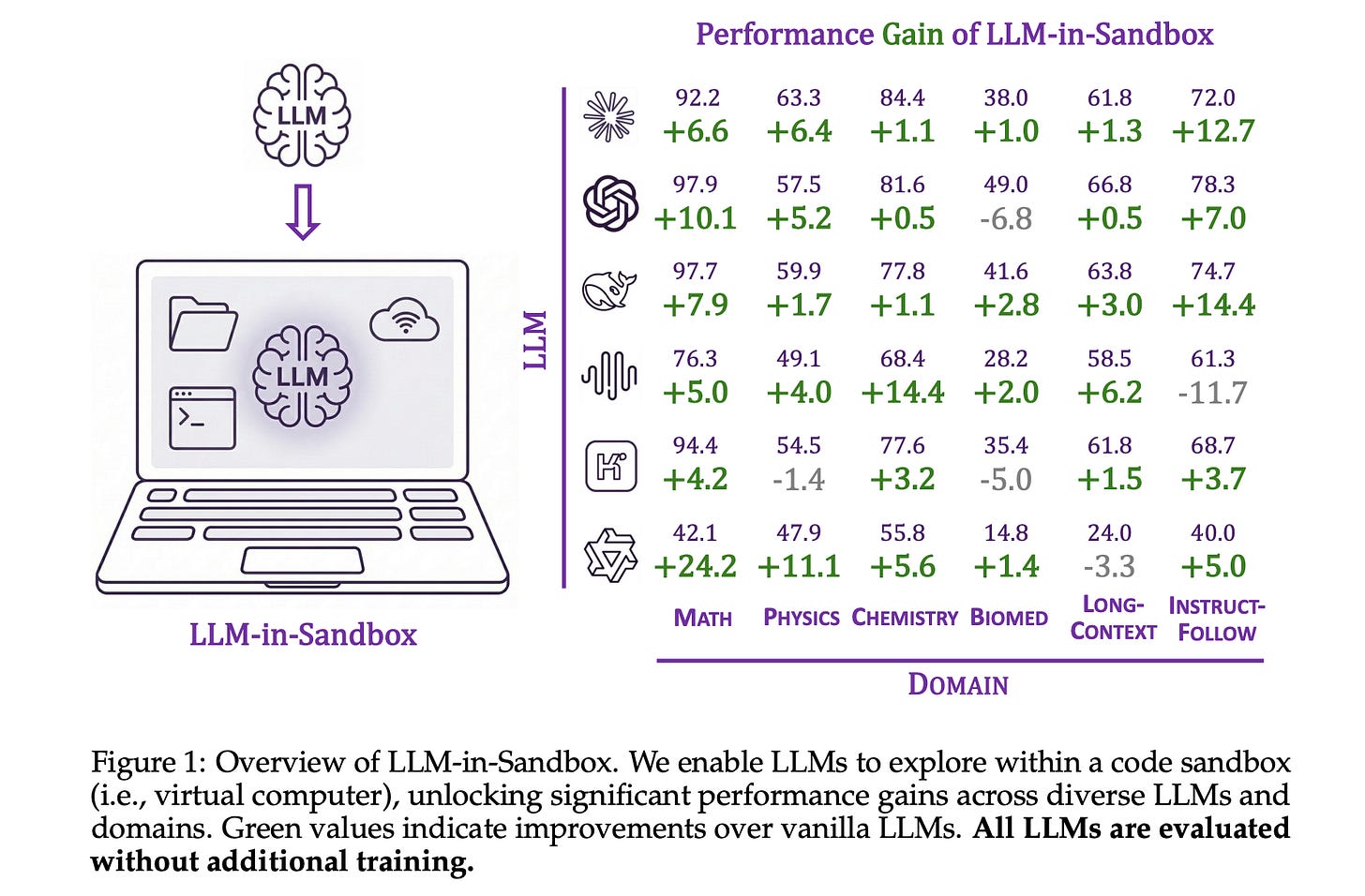
1. LLM-in-Sandbox Elicits General Agentic Intelligence
This research introduces a framework called LLM-in-Sandbox that enables LLMs to operate and explore within a code sandbox/virtual computer to elicit general intelligence in non-code domains.
Researchers show that strong LLMs, without any extra training, can spontaneously use the code sandbox for non-code tasks. Examples include using file systems, executing scripts, and accessing external resources to acquire knowledge.
These capabilities can be further enhanced using LLM-in-Sandbox-RL, a reinforcement learning method to train LLMs for sandbox exploration using only non-agentic data.
Experiments show that LLM-in-Sandbox, in both training-free and post-trained settings, leads to strong generalization across tasks in mathematics, physics, chemistry, biomedicine, long-context understanding, and instruction-following.
Read more about this research using this link.
Before we move forward, I want to reintroduce you to my book called “LLMs In 100 Images”.
It is a collection of 100 easy-to-follow visuals that explain the most important concepts you need to master to understand LLMs today.
Grab your copy today at a special discount using this link.
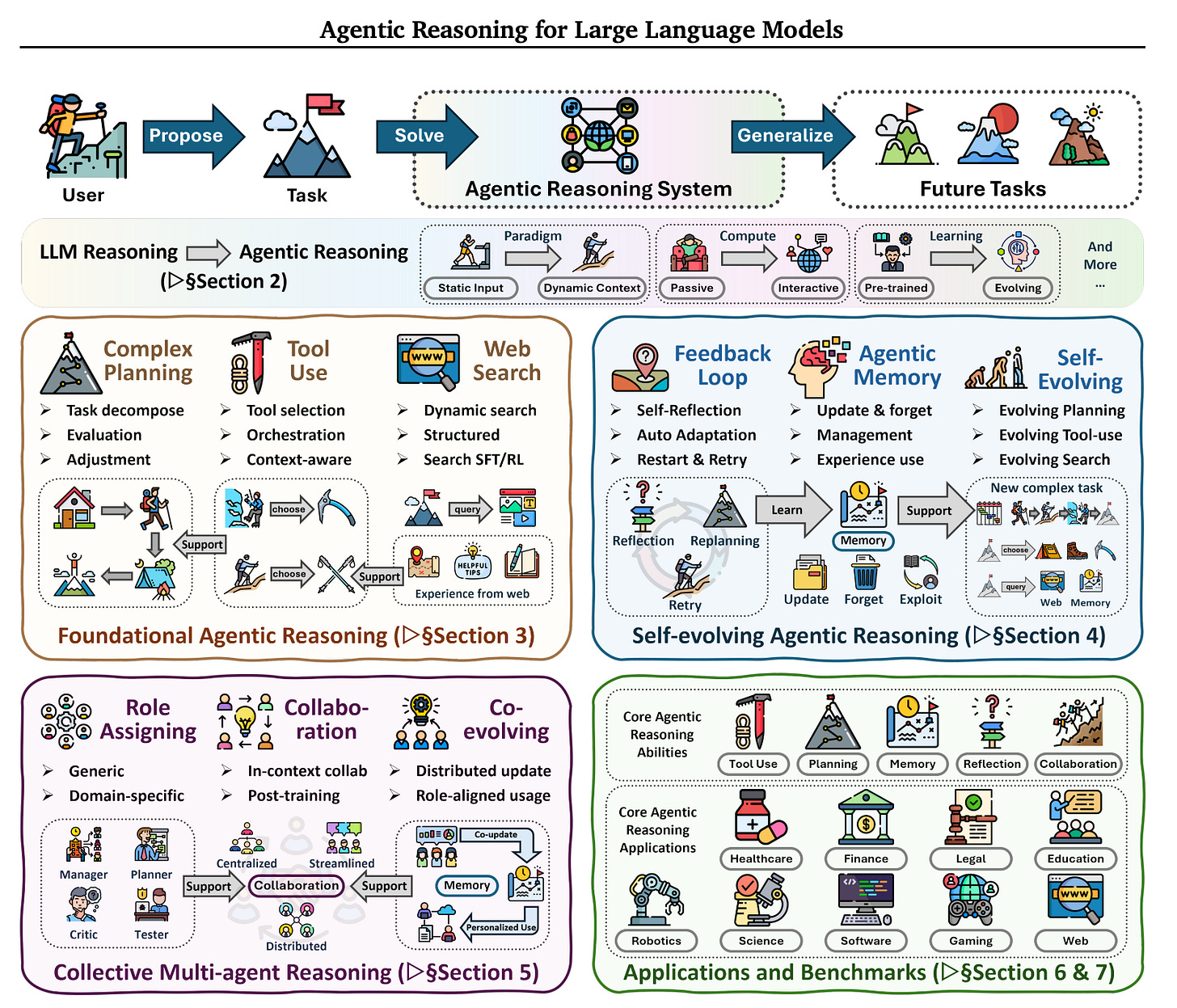
2. Agentic Reasoning for Large Language Models
This research surveys Agentic Reasoning, in which LLMs act as autonomous agents that can plan, act, learn, and reason through continual interaction in their open-ended, dynamic environments.
It organizes Agentic reasoning along three complementary dimensions:
Foundational agentic reasoning: This involves single-agent skills such as planning, tool use, and search in stable environments.
Self-evolving reasoning: This involves how agents improve themselves using feedback, memory, and adaptation in evolving settings.
Collective multi-agent reasoning: This involves how multiple agents coordinate roles, share knowledge, and pursue a shared goal.
Across all layers, the paper distinguishes between the following:
In-context reasoning, which scales test-time interaction using structured orchestration and adaptive workflows
Post-training reasoning, which involves optimization using supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning
The research further reviews agentic reasoning frameworks in real-world applications and benchmarks across science, robotics, healthcare, autonomous research, and mathematics, and offers actionable guidance across different settings.
It also discusses key open challenges, which include personalization, long-horizon interaction, world modeling, scalable multi-agent training, and governance frameworks for real-world deployment.
Read more about this research using this link.
3. D4RT: Teaching AI To See The World In Four Dimensions
This research from Google DeepMind introduces Dynamic 4D Reconstruction and Tracking (D4RT), a feedforward AI model that turns any ordinary video into a 4D representation by reconstructing geometry, motion, and camera pose over space and time.
D4RT uses a transformer-based encoder to create a global scene representation and a flexible query-based decoder that can independently predict the 3D position of any pixel at any time.
This query mechanism decouples space and time, allowing the model to efficiently produce point trajectories, dense point clouds, depth maps, and camera poses from a single representation.
Experiments show that D4RT sets a new state of the art in dynamic 4D reconstruction and tracking, operating up to hundreds of times faster and with greater accuracy than earlier methods.
It also allows for tasks like full-scene reconstruction and object tracking from video at impressive speeds and scalability.
Read more about this research using this link.
A simplified blog post can be found here.
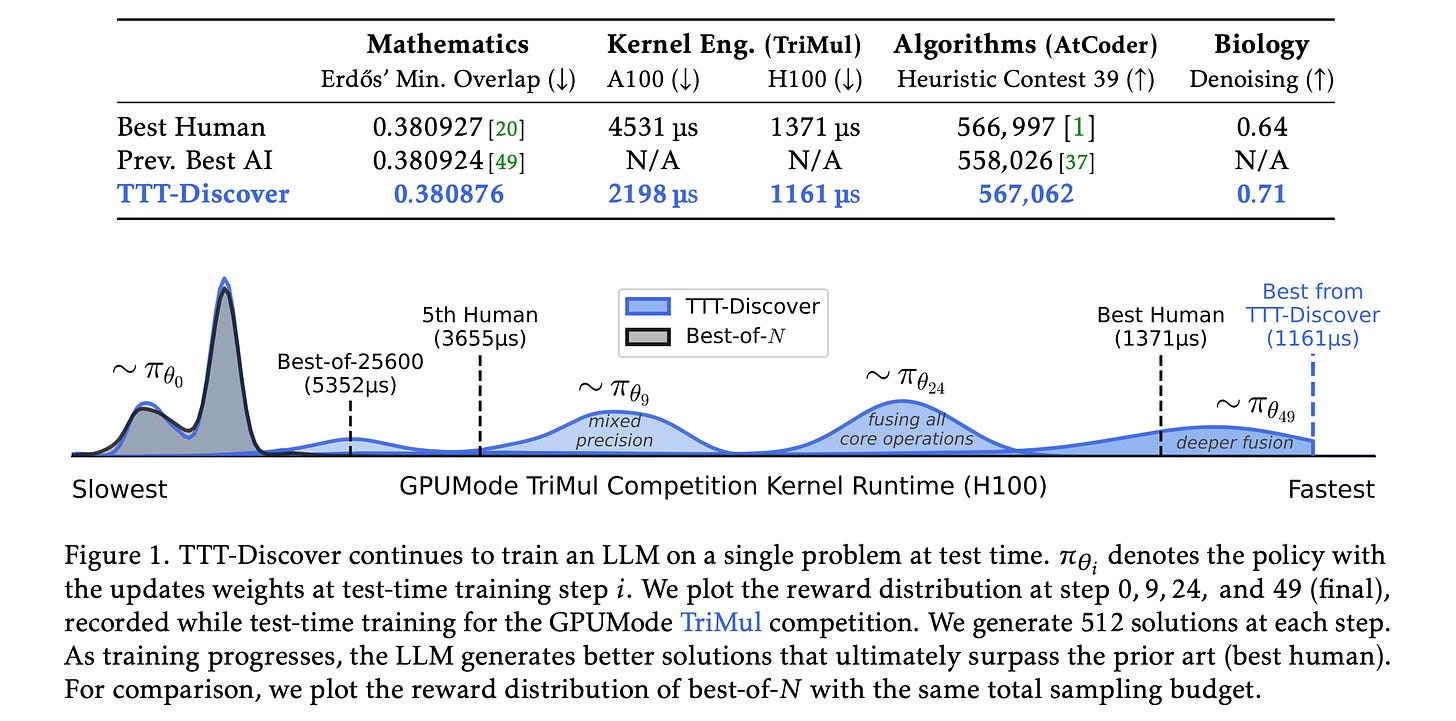
4. Learning to Discover at Test Time
This research introduces a method called Test-Time Training to Discover (TTT-Discover), in which an LLM actively learns during test time to solve a specific problem exceptionally well, finding the single best solution for it rather than achieving average performance across many problems.
Unlike previous approaches, such as AlphaEvolve, which perform search by prompting a frozen LLM, this method uses reinforcement learning at test time, allowing the model to update based on its own experience with the specific task.
Experiments show that TTT-Discover achieves new SOTA results across a range of scientific and optimization challenges in mathematics, GPU kernel design, competitive programming, and biology, using an open model (OpenAI gpt-oss-120b) with practical compute budgets.
Read more about this research using this link.
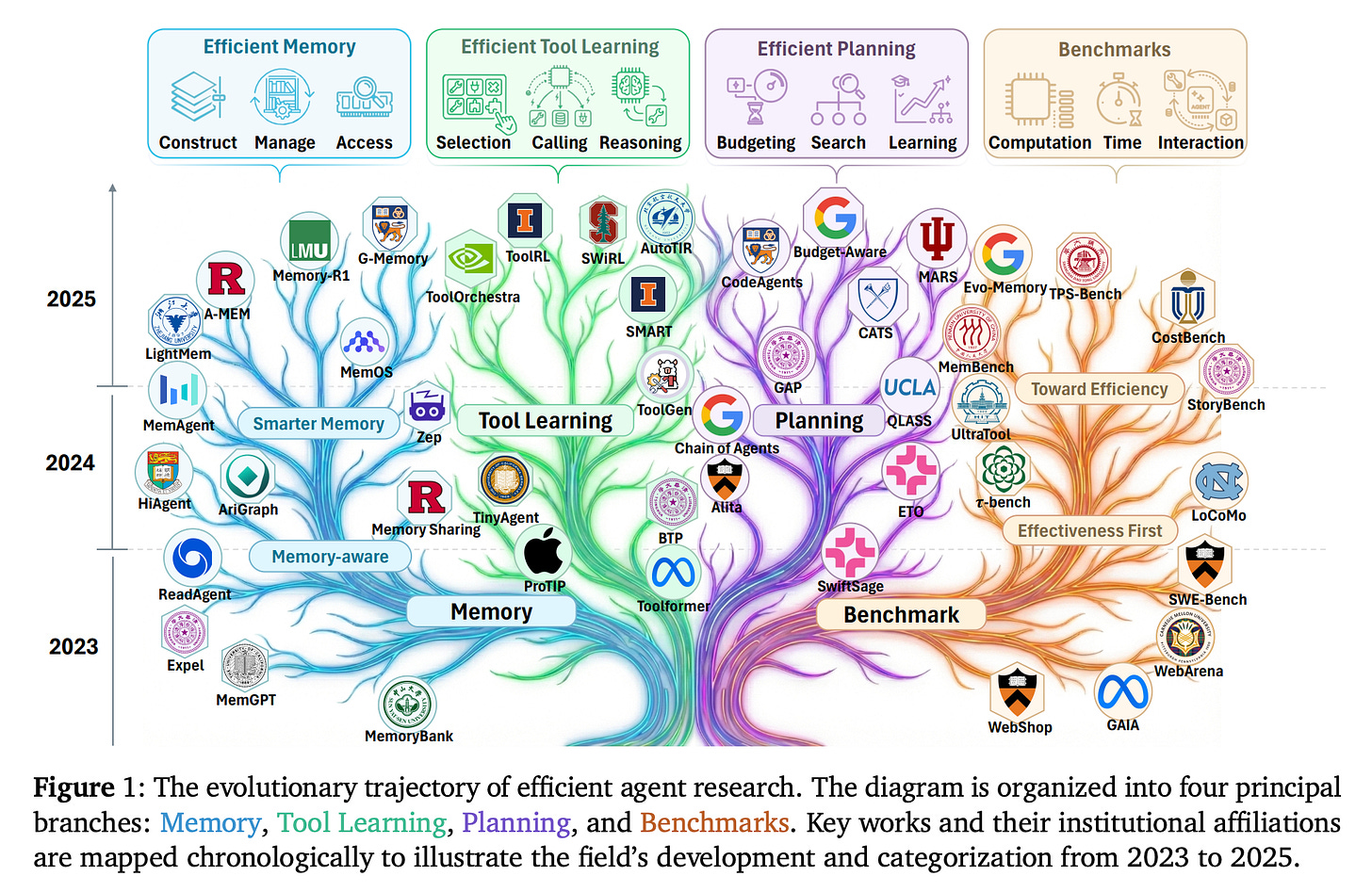
5. Toward Efficient Agents: A Survey of Memory, Tool learning, and Planning
This survey focuses on the often-overlooked problem of efficiency in agentic AI systems.
It examines how the three core components of agentic AI systems, i.e., memory, tool learning, and planning, affect computational metrics like latency, token usage, and reasoning steps.
The authors frame efficiency in two complementary ways as follows, and discuss benchmarks and metrics used to evaluate these trade-offs.
Comparing effectiveness under fixed cost constraints
Comparing costs at similar performance levels
Finally, the survey outlines key challenges and future directions for building efficient, deployable agentic systems.
Read more about this research using this link.
6. 360Anything: Geometry-Free Lifting of Images and Videos to 360◦
This research presents 360Anything, a framework that changes ordinary perspective images and videos into 360° panoramas without needing camera metadata or explicit geometric calibration.
Using pre-trained diffusion transformers, the method views both input and target panoramas as token sequences, learning the mapping purely from data.
It introduces Circular Latent Encoding to remove seam artifacts at equirectangular projection boundaries and achieves SOTA performance in both image and video perspective-to-360° generation.
The framework also shows competitive results in zero-shot field-of-view and camera orientation estimation, showcasing its deep geometric understanding and broader usefulness across computer vision tasks.
Read more about this research using this link.
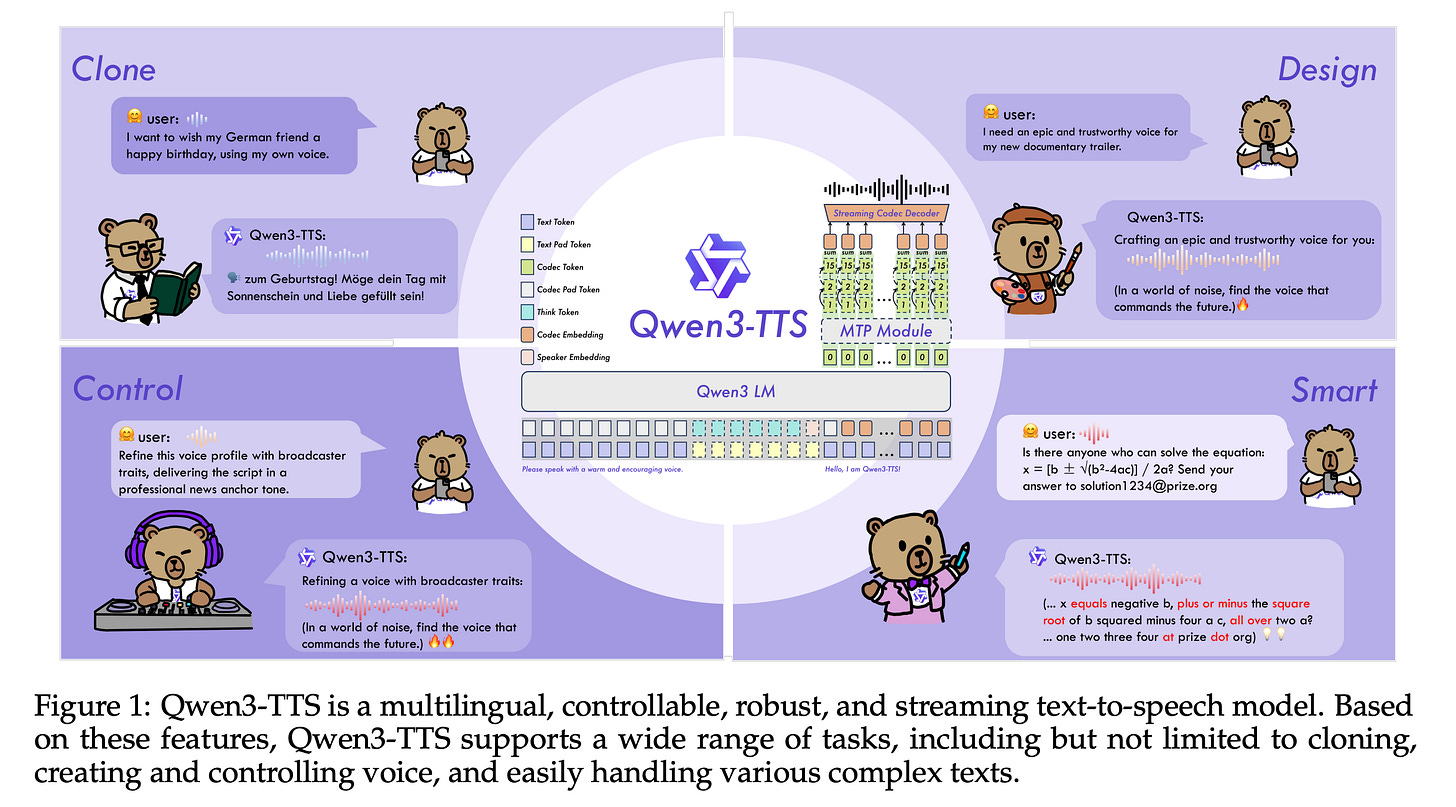
7.Qwen3-TTS Technical Report
This technical report introduces Qwen3-TTS, a new series of text-to-speech (TTS) models from Alibaba.
Qwen3-TTS features a dual-track architecture with two tokenizers: a 25Hz version prioritizing audio quality and semantic richness, and a 12Hz version optimized for ultra-low-latency streaming.
Trained on over 5 million hours of multilingual audio, the model allows fine-grained control of speech characteristics from descriptions, state-of-the-art 3-second voice cloning, efficient streaming synthesis, and high-fidelity generation across multiple languages and speaking styles.
Read more about this research using this link.
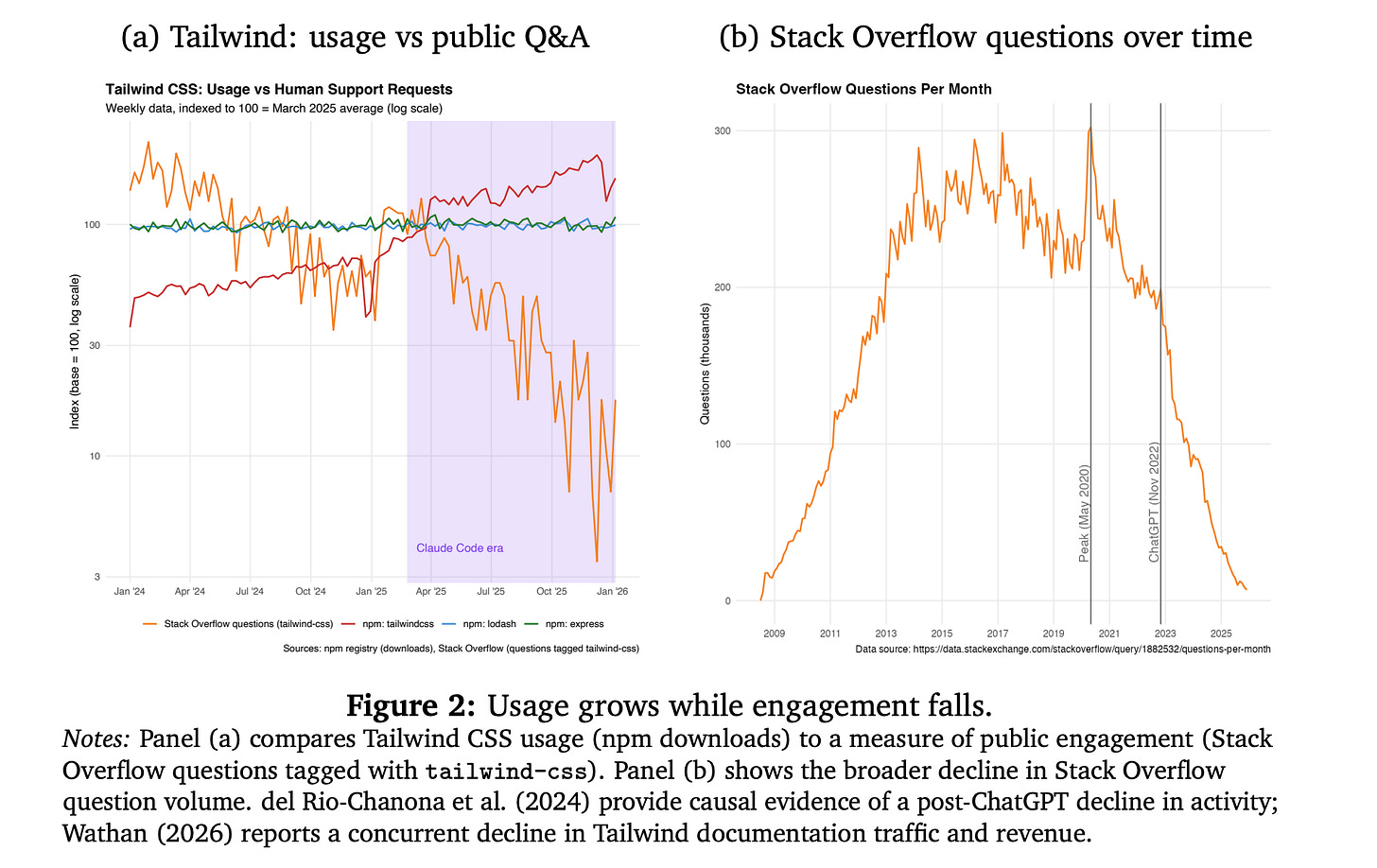
8. Vibe Coding Kills Open Source
This research paper studies how vibe coding impacts the open-source software (OSS) ecosystem.
While vibe coding lowers software development costs and boosts productivity, it also reduces direct user interactions with OSS projects, such as reading documentation, reporting bugs, and communicating with maintainers. Many OSS projects depend on such engagement to maintain themselves and attract contributors.
Widespread adoption of vibe coding could weaken the motivation to contribute, lower the entry and sharing of projects, reduce overall OSS quality, and harm social welfare, even with improved productivity.
The authors explore these effects in an economic equilibrium model and suggest that maintaining OSS at current levels with widespread vibe coding will need significant changes in how maintainers are compensated.
Read more about this research using this link.
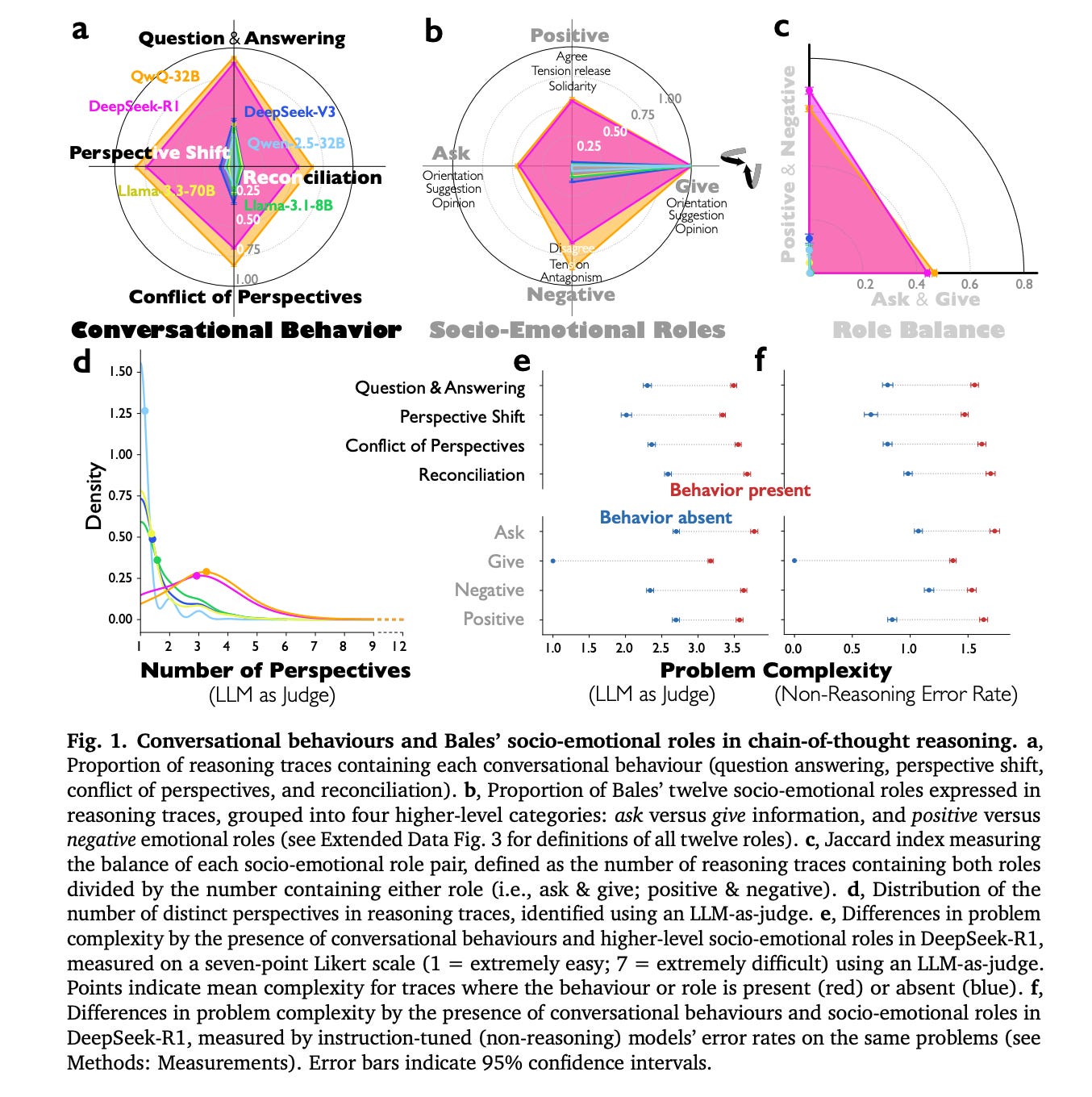
9. Reasoning Models Generate Societies of Thought
This research looks into why reasoning-oriented LLMs perform better than standard instruction-tuned models on complex cognitive tasks.
The authors explain that the improvement does not come only from longer computation or chains of thought. Instead, these models simulate internal interactions similar to multi-agent systems, creating what they call a “Society of thought”.
In this setup, different internal perspectives, each with unique personality traits and domain expertise, engage in discussions. These exchanges involve questioning, shifting perspectives, and resolving conflicts. This process broadens the exploration of solutions and improves reasoning accuracy.
These findings are based on a quantitative analysis of reasoning traces from models such as DeepSeek-R1 and QwQ-32B, which show greater diversity and better conversational structure compared to instruction-tuned models.
Controlled reinforcement learning experiments also indicate that rewarding accuracy alone can lead to new conversational behaviors, and fine-tuning models with conversational scaffolding substantially accelerates reasoning improvement compared to base models and models fine-tuned with monologue-like reasoning.
The findings suggest that structured, dialogue-like internal dynamics, similar to collective intelligence in human groups, enhance AI reasoning.
Read more about this research using this link.
10. LoL: Longer than Longer, Scaling Video Generation to Hour
This research from ByteDance works on a core challenge in long-form video generation: maintaining coherence across very long sequences while avoiding the buildup of errors and scene repetition.
The authors point out a problem known as sink-collapse, in which models repeatedly return to a “sink frame” due to conflicts between Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE) and multi-head attention.
To address this, they introduce a simple technique called multi-head RoPE jitter, which disrupts synchronization across attention heads and stops long-horizon degradation.
Their approach greatly improves stability and quality, leading to real-time, streaming, and effectively infinite-length video generation.
As an illustration of this robustness, the authors generate continuous videos up to 12 hours in length, which is among the longest publicly demonstrated results in streaming video generation to date.
Read more about this research using this link.
If you want to get even more value from this publication, become a paid subscriber.
Get access to all valuable lessons, such as: